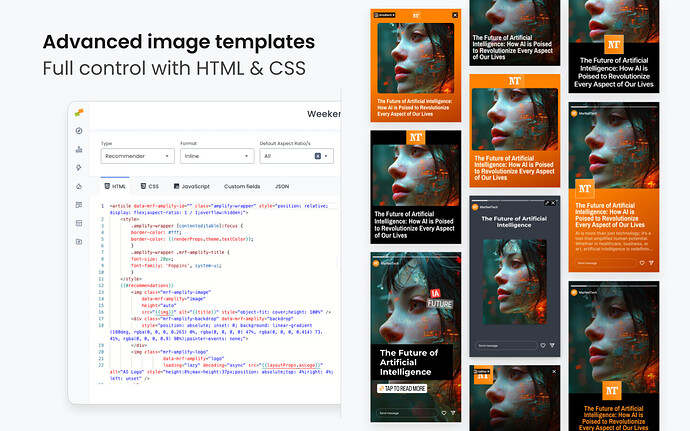
Build HTML and CSS templates that Amplify converts into social media images. Your layouts define how articles appear when shared to Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, and other platforms.
Master Amplify, step by step
The video below is an excerpt from the Amplify Fundamentals course.
![]() Discover more learning paths on Marfeel Academy.
Discover more learning paths on Marfeel Academy.
Layout Anatomy
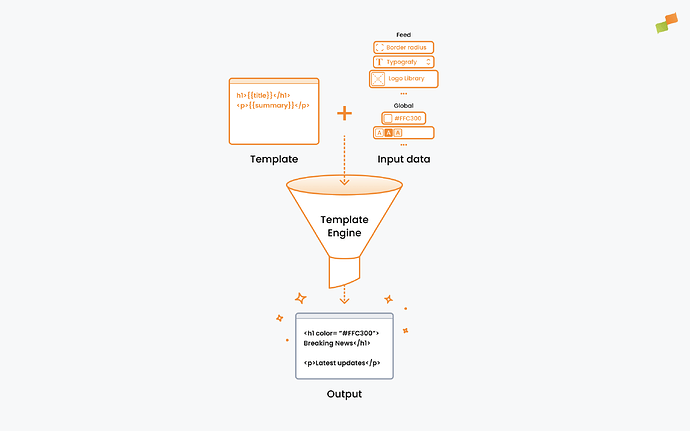
Every Amplify layout consists of three parts:
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| HTML Template | Structure and content placement. Uses Trimou templating to inject article data and mark interactive elements in the layout editor. |
| CSS Template | Visual styling. Also uses Trimou templating to inject colors, fonts, and other configurable properties. |
| Layout Properties | Configurable variables each layout can declare. Admins set values for these properties in Feed Appearance or Global Appearance panels. Access them via {{layoutProps.*}}. Reserved keys (typography, colors, logo) are available by default. |
Layout Configuration
Before writing templates, configure your layout in the Layout Editor header:
| Setting | Options | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Social | Must be “Social” for Amplify layouts |
| Format | Post, Link In Bio | Where the layout can be used |
| Aspect Ratio | Square, Story, Portrait, etc. | Which aspect ratios this layout supports (Post format only) |
Rendering Process
At render time, Amplify merges article data, feed appearance and global appearance settings into the template, then captures the result as an image:
- Your template loads with article data and settings injected
- The HTML/CSS is rendered
- A screenshot is captured
- The image posts to the target platform
Constraint: No client-side JavaScript. Your layout must render correctly on initial page load.
Template Data
Before building templates, understand what data is available to inject.
Article Properties
These values inject automatically from the article being shared:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
{{title}} |
Article headline |
{{description}} |
Article excerpt or meta description |
{{img}} |
Featured image URL |
{{url}} |
Article URL |
{{sections}} |
Article sections/categories |
{{authors}} |
Article author(s) |
Layout Properties (Custom Fields)
Each layout can declare its own Custom Fields—configurable parameters that control the layout’s appearance. Admins set values for these fields in the Feed Appearance or Global Appearance panels, making layouts customizable without code changes.
Reference them in templates with {{layoutProps.<key>}}.
Reserved keys are available by default on every layout. They automatically sync with organization-wide branding settings:
| Category | Keys | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Typography | typographyFamilyName, typographyWeight, typographySize, textAlignment |
Weight: 400, 500, 600, 700Alignment: left, center, right |
| Colors | color, accentColor |
HEX format (e.g., #111111) |
| Logo | logoImg, logoAlignment |
URL, alignment values |
| Image | borderRadius |
Number (pixels) |
| Avatar | avatarImg, avatarAlignment |
Link in Bio only |
Beyond reserved keys, layouts can declare additional custom fields for layout-specific needs (e.g., a secondary color, custom label text, or alternate logo position).
Settings Inheritance
Values cascade through three levels:
Feed Appearance → Global Appearance → Layout Custom Fields
- Feed Appearance: Styling overrides for a specific social feed (e.g., your Instagram account)
- Global Appearance: Organization-wide defaults that apply to all feeds
- Layout Custom Fields: Default values declared in the layout itself, used when neither level above sets a value
Feed-level settings take precedence over global settings, which take precedence over layout defaults. This lets you customize individual feeds while maintaining organization-wide defaults.
Custom Field Types
When defining Custom Fields for your layout, you can use these field types:
| Type | UI Presented |
|---|---|
| Text input | Single-line text field |
| Rich text | Multi-line with formatting |
| Link | URL input field |
| Image | Image picker/uploader |
| Color | Color picker |
| Text styles | Font weight, size, alignment controls |
| Dropdown | Selection from predefined options |
HTML Templating
HTML templates use Trimou syntax to inject article data and layout properties into your markup.
Base Structure
Every layout requires this wrapper:
<article data-mrf-amplify-id="your-layout-name" class="amplify-wrapper">
{{#each content.posts}}
<!-- Your layout content here -->
{{/each}}
</article>
| Attribute | Purpose |
|---|---|
data-mrf-amplify-id |
Unique identifier for your layout |
class="amplify-wrapper" |
Required wrapper class |
{{#each content.posts}} |
Iterates over article data |
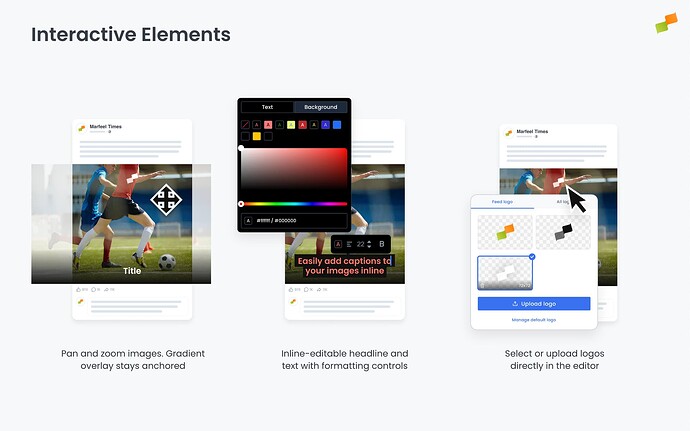
Interactive Elements
The data-mrf-amplify attribute marks elements that social media managers can visually manipulate directly when creating a post.
Text elements (title, description, sections, authors) become inline-editable. Clicking the text opens a visual editor where managers can:
- Edit the text directly on the layout
- Adjust typography (font weight, size)
- Change text color
- Modify alignment
Image elements (image, logo) become interactive canvases. Managers can:
- Zoom in/out to adjust framing
- Pan to reposition the focal point
- Drag and drop to replace the image
| Value | Element Type | Editor Behavior |
|---|---|---|
title |
Text | Inline-editable headline with formatting controls |
description |
Text | Inline-editable excerpt with formatting controls |
sections |
Text | Inline-editable category/section label |
authors |
Text | Inline-editable byline |
image |
Image | Drag-and-drop replacement, zoom, pan |
logo |
Image | Drag-and-drop replacement, zoom, pan |
backdrop |
Layer | Gradient overlay anchored to image bottom. Stays fixed when the image is resized, zoomed, or panned. |
Example:
<h2 class="mrf-amplify-title"
data-mrf-amplify="title"
contenteditable="true">{{title}}</h2>
<img class="mrf-amplify-image"
data-mrf-amplify="image"
src="{{img}}"
alt="{{title}}" />
{{#isNotNull layoutProps.logoImg}}
<img class="mrf-amplify-logo"
data-mrf-amplify="logo"
src="{{layoutProps.logoImg}}"
alt="Logo" />
{{/isNotNull}}
Text Editing Options
Add contenteditable to text elements for inline editing in the Layout Editor:
| Value | Behavior | When to use |
|---|---|---|
contenteditable="true" |
Allows editing with full formatting | When users need bold, italic, or other inline styles |
contenteditable="plaintext-only" |
Strips formatting when pasting text | Most cases—prevents copied styles from breaking your typography |
Example:
<!-- Title: plaintext-only keeps your typography clean -->
<h2 class="mrf-amplify-title"
data-mrf-amplify="title"
contenteditable="plaintext-only">{{title}}</h2>
<!-- Description with rich text: allows bold/italic for emphasis -->
<p class="mrf-amplify-description"
data-mrf-amplify="description"
contenteditable="true">{{description}}</p>
Image Aspect Ratio Configuration
The data-mrf-aspect-ratio attribute defines the aspect ratio at which the image renders, including any masking or cropping.
Syntax: fallback, format:cache-key, format:cache-key
<img data-mrf-aspect-ratio="stories, square:square, landscape:landscape" ... />
How it works:
stories= fallback cache key (used when no format matches)square:square= when layout format issquare, usesquareas the cache keylandscape:landscape= when layout format islandscape, uselandscapeas the cache key
The cache key matters. When a social media manager adjusts an image (zoom, pan, reframe), those adjustments are stored using the cache key. If they switch to a different layout that returns the same cache key, their adjustments carry over automatically.
Example: If two layouts both use square:square, image adjustments made in one layout appear in the other—no rework needed.
Advanced: The format and cache key don’t have to match. Using square:landscape means: when the layout format is square, use landscape as the cache key. This shares image adjustments with other layouts that also use landscape as their cache key.
Available values: square, portrait, landscape, stories (matches the Layout Editor’s Aspect Ratio dropdown).
CSS Templating
CSS files use the same Trimou syntax as HTML templates. This lets you inject layout properties into your styles.
Example:
.mrf-amplify-title {
color: {{layoutProps.accentColor}};
font-family: {{#ifs layoutProps.typographyFamilyName}}{{layoutProps.typographyFamilyName}}, {{/ifs}}system-ui;
}
For full Trimou syntax reference (conditionals, switch/case, loops), see Templating Syntax.
Custom Typography
Using custom fonts requires two steps:
- Declare the font with
@font-face - Use it in your layout via CSS
Step 1: Declare fonts in Global Appearance
Add @font-face declarations in the Custom CSS block of Global Appearance settings:
@font-face {
font-family: 'Your Font';
src: url('font-url.woff2');
font-weight: 400 900; /* For variable fonts, specify the weight range */
}
Step 2: Configure typography settings
In Global or Feed Appearance, set the default values for:
typographyFamilyName– which font to usetypographyWeight– font weighttypographySize– font sizetextAlignment– text alignment
These values flow into your layout via settings inheritance and are available as {{layoutProps.*}} for substitution.
CSS Variable Fallbacks (CSS Technique)
Use duplicate declarations to create fallbacks:
.amplify-wrapper {
background-color: var(--mrf-dominant-color);
background-color: {{layoutProps.color}};
}
CSS applies the last valid declaration. If layoutProps.color has a value, it wins. If it renders empty (invalid CSS), the browser ignores that line and keeps --mrf-dominant-color (automatically extracted from the article image).
Responsive CSS Patterns
Different social networks accept different aspect ratios—Instagram Stories use 9:16, feed posts work best at 4:5, and landscape 16:9 suits YouTube thumbnails. The more screen real estate an image occupies, the more visibility it gets and the higher the probability of engagement.
Building a separate layout for each aspect ratio is tedious. Instead, use CSS container queries to create responsive layouts that adapt to multiple formats automatically. Unlike media queries (which respond to viewport size), container queries respond to the layout’s actual dimensions—exactly what you need since Amplify renders layouts at fixed sizes for each platform.
Container Setup
Define a named container on your wrapper:
.amplify-wrapper {
container-name: classic;
container-type: size;
}
Aspect Ratio Queries
Target specific aspect ratios with @container:
/* Portrait (Stories) - hide logo, adjust spacing */
@container classic ((aspect-ratio > 8/16) and (aspect-ratio < 10/16)) {
.mrf-amplify-logo {
display: none;
}
.mrf-amplify-title-container {
margin-bottom: 16cqw;
}
}
/* Landscape (16:9) - smaller text */
@container classic ((aspect-ratio > 15/9) and (aspect-ratio < 17/9)) {
.mrf-amplify-title {
font-size: 3.5cqw;
}
}
Container Query Units
Use cqw (container query width) and cqh (container query height) for responsive sizing:
| Unit | Description |
|---|---|
cqw |
1% of container width |
cqh |
1% of container height |
.mrf-amplify-logo {
top: 5cqw;
height: 7.25cqw;
}
.mrf-amplify-border {
width: 88cqw;
height: 90cqh;
}
Link in Bio Properties
Link in Bio layouts have additional data:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
{{avatar}} |
Profile avatar image URL |
{{link}} |
Destination URL |
{{linkText}} |
Button text |
Complete Example
A minimal but complete layout showing both HTML and CSS files working together.
HTML Template
<article data-mrf-amplify-id="minimal-example" class="amplify-wrapper">
{{#each content.posts}}
<div class="mrf-amplify-image-container">
<img class="mrf-amplify-image"
data-mrf-amplify="image"
data-mrf-aspect-ratio="landscape, portrait:square, stories:stories"
src="{{img}}"
alt="{{title}}"
/>
<div class="mrf-amplify-backdrop"></div>
</div>
{{#isNotNull layoutProps.logoImg}}
<img class="mrf-amplify-logo"
data-mrf-amplify="logo"
src="{{layoutProps.logoImg}}"
alt="Logo"
/>
{{/isNotNull}}
<div class="mrf-amplify-title-container">
<h2 class="mrf-amplify-title"
data-mrf-amplify="title"
contenteditable="plaintext-only">{{title}}</h2>
</div>
{{/each}}
</article>
CSS Template
body {
--mrf-dominant-color: #444;
}
.amplify-wrapper {
container-name: minimal-example;
container-type: size;
position: relative;
height: 100%;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
font-family: {{#ifs layoutProps.typographyFamilyName }}{{layoutProps.typographyFamilyName}},{{/ifs}}system-ui;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
overflow: hidden;
box-sizing: border-box;
background: var(--mrf-dominant-color);
{{#isNotNull layoutProps.color}}
background: {{layoutProps.color}};
{{/isNotNull}}
}
.mrf-amplify-image-container {
position: relative;
overflow: hidden;
flex: 1;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.mrf-amplify-image {
object-fit: cover;
height: 100%;
flex: 1;
}
.mrf-amplify-backdrop {
pointer-events: none;
position: absolute;
inset: 0;
background: linear-gradient(180deg, transparent 70%, rgba(0,0,0,0.6) 100%);
}
.mrf-amplify-logo {
object-fit: cover;
position: absolute;
top: 5cqw;
height: 7.25cqw;
{{#choose}}
{{#when "layoutProps.logoAlignment eq 'left'"}}
left: 6cqw;
{{/when}}
{{#when "layoutProps.logoAlignment eq 'right'"}}
right: 6cqw;
{{/when}}
{{#otherwise}}
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
{{/otherwise}}
{{/choose}}
}
.mrf-amplify-title-container {
padding: 6cqw;
}
.mrf-amplify-title {
margin: 0;
color: {{layoutProps.accentColor}};
font-weight: {{layoutProps.typographyWeight}};
font-size: calc({{layoutProps.typographySize}} * 1px);
line-height: 1.1;
text-align: {{layoutProps.textAlignment}};
text-wrap: balance;
}
/* Portrait (Stories) */
@container minimal-example ((aspect-ratio > 8/16) and (aspect-ratio < 10/16)) {
.mrf-amplify-logo { display: none; }
.mrf-amplify-title-container { padding-bottom: 16cqw; }
}
/* Landscape (16:9) */
@container minimal-example ((aspect-ratio > 15/9) and (aspect-ratio < 17/9)) {
.mrf-amplify-logo { display: none; }
.mrf-amplify-title { font-size: 3.5cqw; }
}
Enable or Disable Layouts
Admins toggle layouts without deleting them:
- Enabled: Available for social media managers to select
- Disabled: Hidden from selection but preserved
Going Deeper
- Layout Editor: The visual interface for building and testing layouts
- Templating Syntax: Mustache tags, conditionals, and data fields
- Recommender Layouts: Customizing article recommendations
Become a Marfeel Amplify expert
Learn how to publish smarter, automate sharing, and optimize your social strategy with our Marfeel Amplify Course.
Workflow-focused training
Automation strategies
Certificate of completion included
![]() Start now on Marfeel Academy.
Start now on Marfeel Academy.