As a content creator, it’s important to understand how visitors access your site and where they come from. This information can help you make informed decisions about your content strategy and optimize your website for maximum visibility.
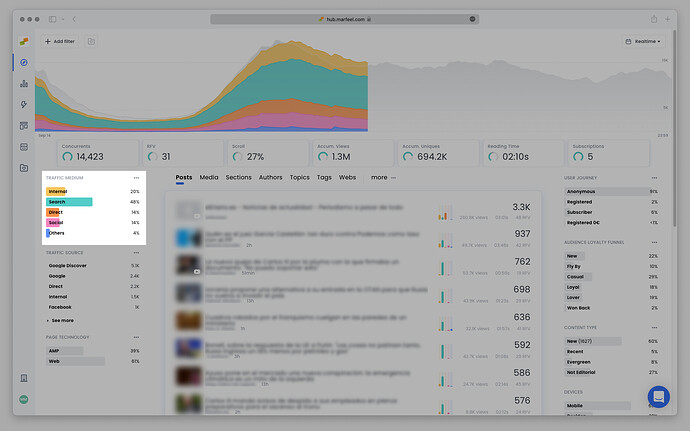
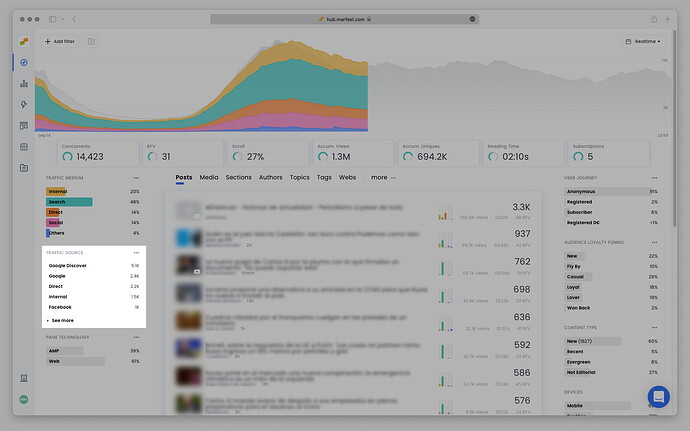
Marfeel provides insights into these questions with the metricsTraffic medium and Traffic source. Each traffic source pertains to a broader traffic medium. For example, for a visitor who accesses your website via a Google search result, “Google” is the traffic source and “Search” is the traffic medium.
| Medium | Source |
|---|---|
| Social | Facebook, Twitter, Dark social, etc |
| Search | Google, Bing, Google Discover, Google News, Google Showcase, etc |
| Internal | Home page modules, navigation bars, hyperlinks, etc |
| Direct | No source attribution (see below) |
| Others - Referral | Taboola, another site within your network, etc |
| Others - Push | Onesignal, etc |
| Others - Paid | Facebook ads, Google Adwords, etc |
While traffic sources and traffic mediums are related, they answer different questions and provide different insights into your website’s visitor behavior. Traffic sources show the “where” (a link on Facebook), while traffic mediums explain the “how” (scrolling through social media).
Become a Realtime expert
Learn how to monitor your live audience, spot trends early, and make data-informed editorial decisions with our Realtime Fundamentals Course.
Real-time decision making
Actionable use cases
Certificate of completion included
![]() Start now on Marfeel Academy.
Start now on Marfeel Academy.
What is a Traffic Medium?
Traffic medium refers to the type of channel used by the visitor to access your website. It answers the question, “how did the visitor access the website?”
Examples of traffic mediums include:
- Search: Visitors who found your website through an organic (unpaid) search engine result.
- Paid: Visitors who found your website through a paid search engine result, such as a Google AdWords campaign.
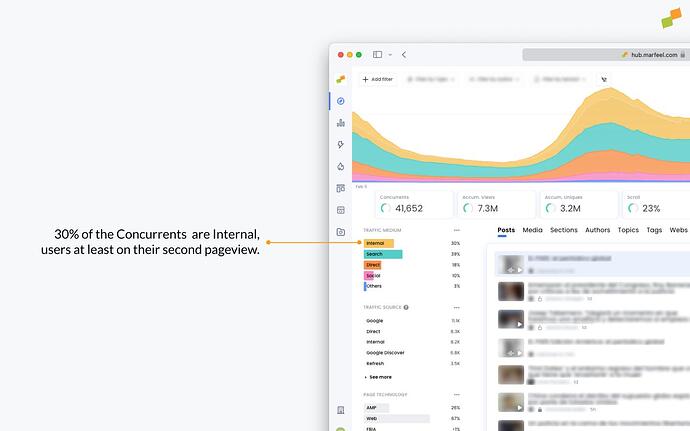
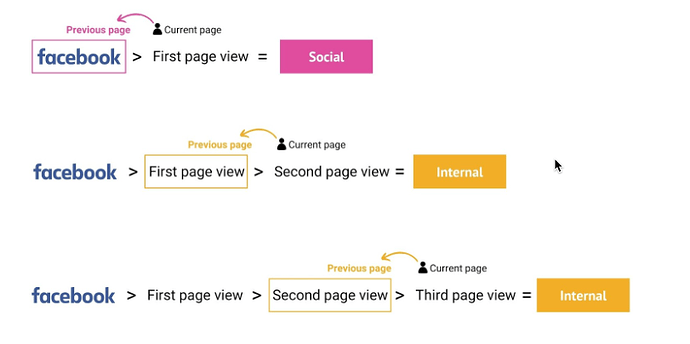
- Internal: Also known as recirculation traffic, internal traffic is the number of users who currently are at least on their second page view of your website. Read more about internal traffic.
- Direct: Visitors who typed your website’s URL directly into their browser or clicked on a bookmark.
- Social: Visitors who accessed your website from a social media platform, such as Facebook or Twitter.
- Email: Visitors who accessed your website via an emailed link.
- Referral: Visitors who accessed your website via a link on another website.
What is a Traffic Source?
Traffic source refers to the origin of a visitor’s journey to your website. It answers the question, “where did the visitor come from?”
Examples of traffic sources include:
- Home page module: Marfeel identifies all the recirculated traffic from a given module on the home page. Other examples of
Internaltraffic sources include infinite scroll, side bars, navigation bars, recommended articles, etc. Read more about internal traffic. - Taboola: Indicates the visitors who accessed your content via a Taboola-generated recommendation. The traffic medium in this case would be
Referral. - Google Discover: The visitor found your content via their Discover feed. The traffic medium is
Search. - Facebook: When a visitor clicks an unsponsored link on Facebook, the traffic medium attribution is
Social. However, if the visitor clicks on a link in a Facebook ad, the source remains Facebook, but the traffic medium isPaid. - Google AdWords: A type of
Paidtraffic, visitors who access your site via a sponsored link on Google will be attributed to this source.
Master Realtime, step by step
The video below is an excerpt from the Realtime Fundamentals course.
![]() Discover more learning paths on Marfeel Academy.
Discover more learning paths on Marfeel Academy.
Internal Traffic
Also known as recirculation traffic, internal traffic is the number of users who currently are at least on their second page view of your website. These users have clicked on an internal recirculation link to access the content they are viewing at that moment. Marfeel allows you to see which users interaction, module or link generate internal traffic.
With Marfeel, traffic mediums update in real time. For example, if a user clicks on an article in their Facebook feed and lands on your website, the traffic medium of that page is attributed to “Social”. However, if that user then clicks on a second page on your site, the traffic medium attribution of the second page will be “Internal”.