Feeds are a fundamental component of the Content Recommender system, allowing you to control and customize the content that is recommended to your users. By combining different recommendation engines and even integrating content from other accounts, feeds offer flexibility and precision in delivering the most relevant content to your audience.
This guide explains what feeds are, how they can be configured, and provides practical use cases to help you leverage feeds effectively in your content strategy.
1. What Are Feeds?
In the context of the Content Recommender system, feeds are sources of content that determine which articles are recommended to users. Feeds can:
- Utilize different recommendation engines, such as most read, latest, trending, similar, highest CTR, personalized, or balanced.
- Combine multiple feeds to create a blended recommendation experience.
- Include remote feeds from other accounts, allowing content sharing between different publishers or sites.
By configuring feeds, you can tailor the recommender to deliver content that aligns with your site’s goals and your users’ interests.
2. Configuring Feeds
Feeds can be configured in two primary ways using the Distribution field:
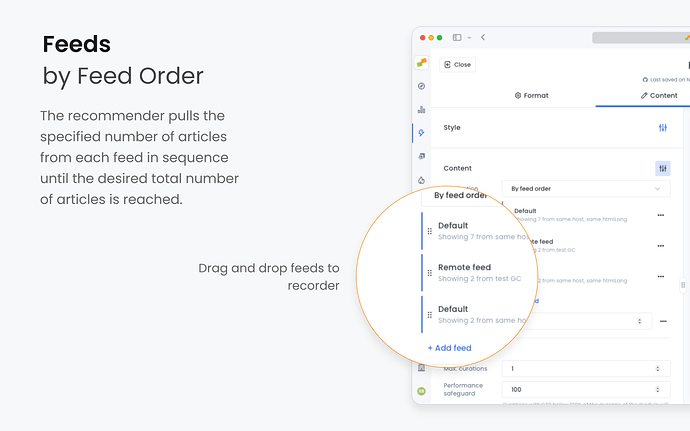
2.1. By Feed Order
Feeds are prioritized in a specific order. The recommender pulls the specified number of articles from each feed in sequence until the desired total number of articles is reached.
How It Works
- Sequential Filling: The system fills the recommendation slots by taking articles from the first feed until it runs out or reaches its limit.
- Proceed to Next Feed: If more slots are available, it moves to the next feed in the order.
Example
You have two feeds:
- Feed 1: Contains 2 articles.
- Feed 2: Contains 4 articles.
You want a total of 3 articles in your recommender.
Result: The recommender will take 2 articles from Feed 1 and 1 article from Feed 2.
Use Case
Prioritizing Content: Ensure that the most important content (e.g., from a certain section) appears first.
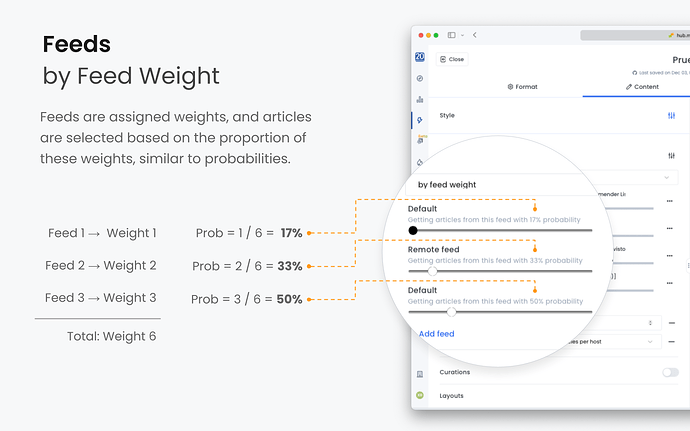
2.2. By Feed Weight
Feeds are assigned weights, and articles are selected based on the proportion of these weights, similar to probabilities.
How It Works
- Weighted Selection: Each feed’s weight determines the likelihood of its articles being selected.
- Probability Calculation: The probability of selecting an article from a feed is its weight divided by the total weight of all feeds.
Example
You have two feeds:
- Feed 1: Weight of 1.
- Feed 2: Weight of 3.
Total Weight: 1 + 3 = 4.
Probabilities:
- Feed 1: 1/4 = 25% chance.
- Feed 2: 3/4 = 75% chance.
Each article slot is filled by randomly selecting from the feeds based on these probabilities.
Use Case
Balanced Diversity: Blend content types while giving preference to certain feeds (e.g., more weight to personalized content over generic content).
3. Ensuring Content Diversity and Balance
To guarantee a diverse and balanced set of recommendations, you can restrict the number of articles from specific categories within the resulting feed:
- Sections: Limit articles from any one section.
- Hosts: Control content from different domains or subdomains.
- Authors: Prevent over-representation of a single author’s work.
- Topics/Tags: Ensure a variety of subjects are covered.
- Folders: Manage content groupings based on custom criteria.
Example:
- Section Restriction: Limit the recommender to include no more than one article per section.
- Author Restriction: Ensure that no single author has more than two articles in the recommendations.
To ensure that users are consistently presented with fresh and engaging content, the recommender system automatically excludes articles that a user has already read from their recommendations. This feature maximizes recirculation by encouraging users to explore new content rather than revisiting what they’ve already seen.
Limiting Total Number of Articles
You can set a maximum number of articles for the entire feed to ensure the recommendations fit within the visual design of your site and do not overwhelm users.
- Visual Consistency: Prevents layout issues by keeping the number of recommendations predictable.
- User Experience: Helps maintain a clean and organized appearance.
Example
Set the feed to display a maximum of 5 articles, even if the combined feeds could provide more content.
4. Understanding Remote Feeds
Remote feeds allow you to incorporate content from other sites or publications into your recommender. This feature is particularly useful for large publishers who own multiple sites or for partnerships between different publishers who wish to share content.
- Content Sharing: Remote feeds enable the sharing of content between different accounts or domains.
- Independent Control: The originating site controls the content within the remote feed.
- Seamless Integration: Remote content appears in your recommender alongside your own content.
How Do Remote Feeds Work?
- Originating Site:
- Creates a recommender using their own content.
- Generates a unique recommender ID.
- Receiving Site:
- Creates a new recommender.
- Adds a remote feed by inputting the provided recommender ID from the originating site.
- Configures the feed alongside their own feeds.
Content Control
The originating site (e.g., a Sports publication) has full control over what content is included in their feed.
Any changes or curations made by the originating site are reflected in real-time in the receiving site’s recommender.
Measuring Remote Feeds: Recirculation metrics
Both the originating and receiving sites have access to metrics related to the performance of the remote feed, allowing for data-driven optimization.
- Receiving Site (e.g., News Site): Full Metrics
- Eligible: Number of articles available for recommendation.
- Viewable Impressions: How many times articles were actually viewable by users.
- Clicks: Number of times users clicked on the recommended articles.
- Click-Through Rates (CTRs): The ratio of clicks to viewable impressions.
- Originating Site (e.g., Sports Site): Partial Metrics to avoid disclosing the number of Pageviews from the Receiving site
- Viewable Impressions: Number of times their articles were viewed on the receiving site.
- Clicks: Number of clicks their articles received on the receiving site.
- CTRs: Click-through rates for their content on the receiving site.
The originating site does not see the eligible articles metric from the receiving site to protect the latter’s overall pageview data.
The Benefits of metrics sharing:
- Optimization: The originating site can fine-tune their content and recommendations based on performance data.
- Transparency: Both parties can monitor the effectiveness of the content sharing arrangement.
Advantages of Remote Feeds
- Expanded Content Offering: Provides users with a broader range of content without the need to create it all in-house.
- Cross-Promotion: Increases visibility for both sites, potentially attracting new audiences.
- Real-Time Updates: Changes made by the originating site are immediately reflected in the receiving site’s recommender.
- Control Over Content: Each site maintains control over their own content and how it’s presented.